You can then look up the present value interest factor in the table and use this value as a factor in calculating the present value of an annuity, series of payments. This calculation helps decide if taking the annuity makes more sense than investing a lump sum elsewhere at potentially higher returns. Imagine you’re planning for retirement and expect to receive $10,000 each year for 20 years.
Create a free account to unlock this Template
This factor tells us how much one dollar today will be bookkeeping worth in the future considering compound interest and time value of money. Calculating the present value of a single amount involves figuring out what a future sum of money is worth today. This calculation uses the time value of money, which says that cash in hand now is more valuable than the same amount in the future due to its potential earning capacity. Think of an annuity table as a tool for predicting cash values over time.
Annuity Rates Information
- An annuity is a series of payments that occur at the same intervals and in the same amounts.
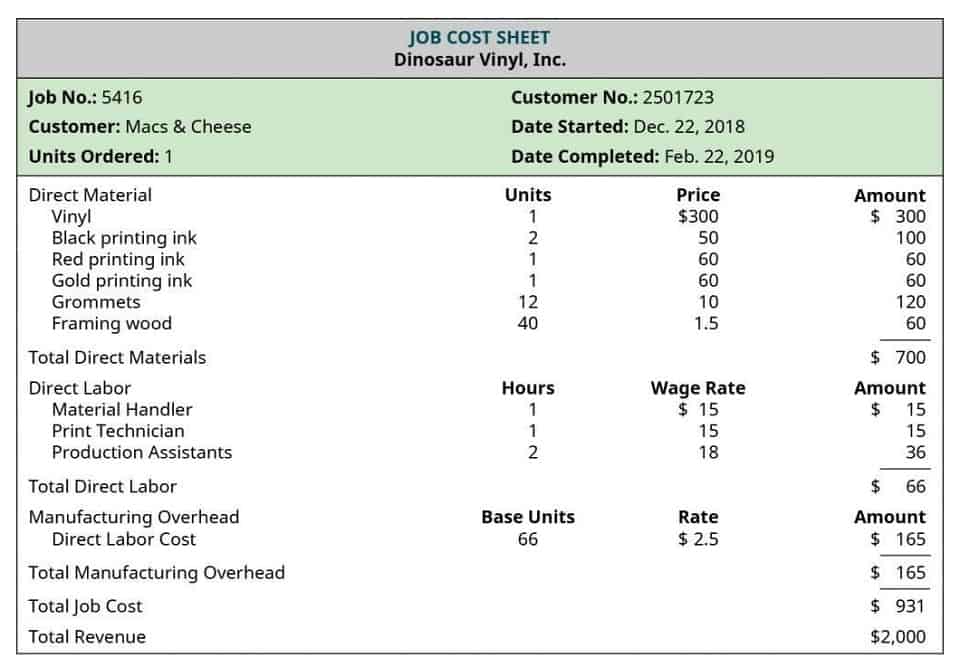
- It shows that $4,329.48, invested at 5% interest, would be sufficient to produce those five $1,000 payments.
- Where i is the interest rate per period and n is the total number of periods with compounding occurring once per period.
- For example, if an individual could earn a 5% return by investing in a high-quality corporate bond, they might use a 5% discount rate when calculating the present value of an annuity.
- Given this information, the annuity is worth $10,832 less on a time-adjusted basis, and the individual should choose the lump sum payment over the annuity.
- An annuity table is a tool for determining the present value of an annuity or other structured series of payments.
- Most people would like to use a dollar today more than a dollar in 10 years regardless of whether the purchasing power is exactly the same.
There are ordinary annuities where payments occur at the end of the period and present value of an annuity due or PVAD where the payments occur at the beginning of the period. The formulas described above make it possible—and relatively easy, if you don’t mind the math—to determine the present or future value of either an ordinary annuity or an annuity due. Such calculations and their results can pv of annuity table add confidence to your financial planning and investment decision-making. The present value of an annuity refers to how much money would be needed today to fund a series of future annuity payments. Or, put another way, it’s the sum that must be invested now to guarantee a desired payment in the future.

Cumulative Rate Table For the Present Value of an Ordinary Annuity of 1
By the same logic, $5,000 received today is worth more than the same amount spread over five annual installments of $1,000 each. Double Entry Bookkeeping is here to provide you with free online information to help you learn and understand bookkeeping and introductory accounting. Think of it as a conversion factor that changes future money into today’s dollars, because money now is worth more than money later. This concept helps make financial decisions like comparing investment options or valuing cash flows from projects. To find this present worth, you apply a discount rate, which adjusts for interest and compounding over time.
Two Types of Annuities
A key component of comparing and evaluating the purchase of an annuity or reviewing the value of an annuity you already own is the present value calculation. The critical assumption of present value is that a dollar today is worth more than a dollar in the future. When comparing or evaluating annuities, present value is a way to place two or more different products on an equal standing and compare their present discounted values. In contrast to the FV calculation, PV calculation tells you how much money would be required now to produce a series of payments in the future, again assuming a set interest rate. Having $10,000 today is better than being given $1,000 per year for the next 10 years because the sum could be invested and earn interest over that decade.
- Most people would prefer to have the money now as they would be able to invest it and earn interest over the year.
- An annuity table provides a factor, based on time, and a discount rate (interest rate) by which an annuity payment can be multiplied to determine its present value.
- There are several ways to measure the cost of making such payments or what they’re ultimately worth.
- Essentially, in normal interest rate environments, a dollar today is worth more than a dollar tomorrow because it has the ability to earn interest and grow with time.
- It’s important to realize that the PVAD tables assume that payments are made at the beginning of each period.
- Pick an interest rate that matches your investment expectations—in this case, let’s say 5%.
Present value annuity due tables are used to provide a solution for the part of the formula shown in red. Additionally this is sometimes referred to as the present value annuity due factor. An annuity is a series of payments that occur over time at the same intervals and in the same amounts.

Best Annuities of 2025
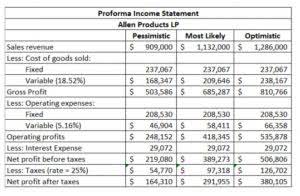
Therefore, there are certain formulas to compute the present value and future value of annuities. The factor is determined by the interest rate (r in the formula) and the number of periods in which payments will be made (n in the formula). In an annuity table, the number of periods is commonly depicted down the left column. Simply select the correct interest rate and number of periods to find your factor in the intersecting cell. That factor is then multiplied by the dollar amount of Accounting for Marketing Agencies the annuity payment to arrive at the present value of the ordinary annuity.
Present Value of an Annuity Formula
Additionally the present value of annuity table is available for download in PDF format by following the link below. Where i is the interest rate per period and n is the total number of periods with compounding occurring once per period. Our article will guide you through using this table to make smart decisions about investments and savings. A Present Value of an Ordinary Annuity Table is a financial tool used to calculate the present value of an ordinary annuity. An annuity specialist will contact you shortly on the provided number.
Using the present value of an annuity table helps us understand what future payments are worth right now. It uses the time value of money to show that cash today beats cash tomorrow. An annuity table helps you understand how much money from regular, equal payments will be worth in the future. It uses the time value of money to show that money now has a different value than the same amount later. The annuity table provides a quick way to find out the present and final values of annuities. However, in the real world, interest rates and time periods are not always discrete.